The rocky life of NASA’s 5 Mars rovers: Images from the red planet
NASA has sent five robotic vehicles to Mars. Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance. Look back at the missions.
Brian Cooper, who will command the Mars Pathfinder rover "Sojourner", uses 3-D glasses on July 1,1997 to operate the mechanical explorer which will give him a three dimensional view of the Martian surface. He will receive pictures of the Martian surface including Sojourner from the camera on the Mars Pathfinder Lander.
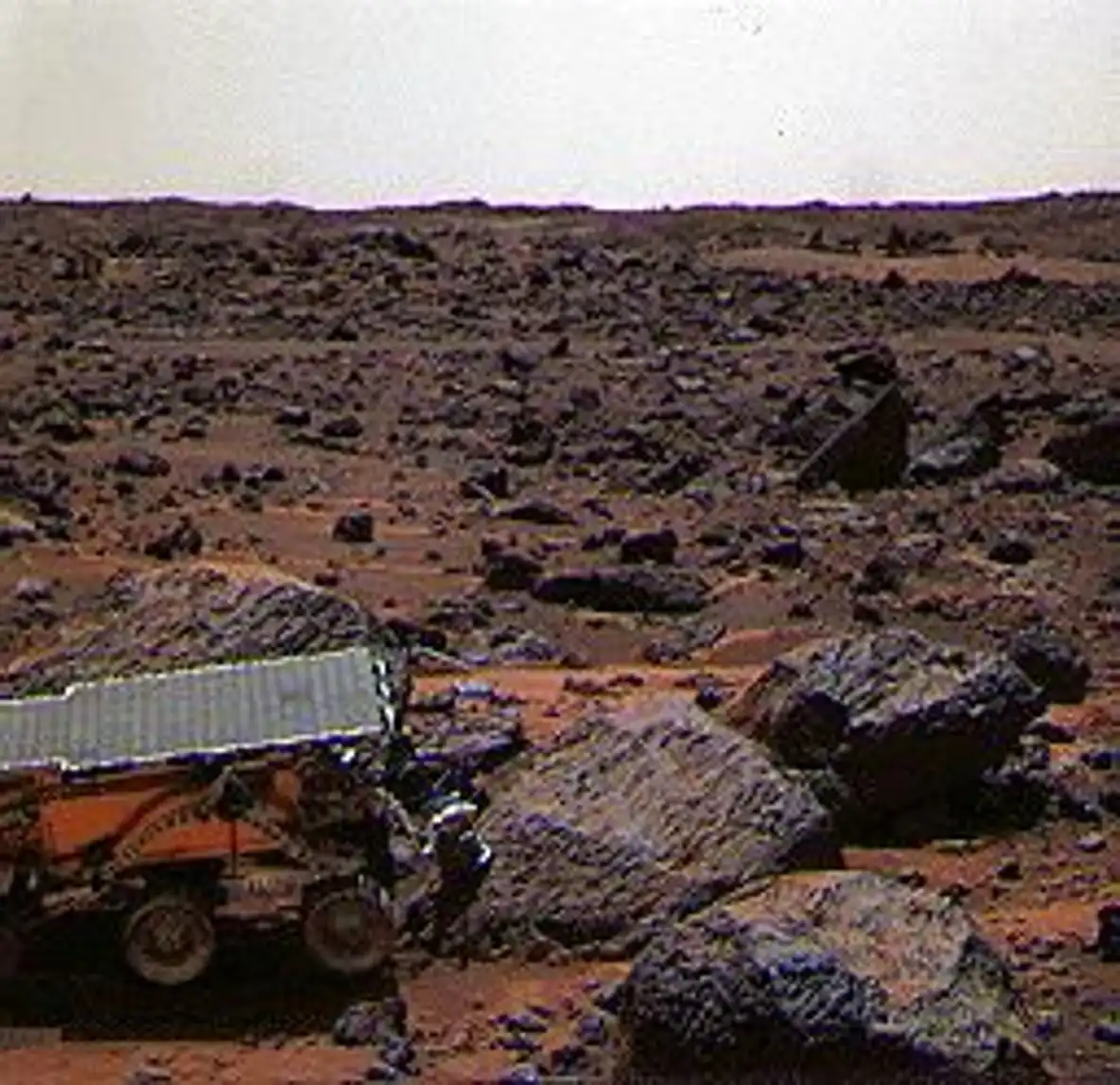

Workers put final touches to the two new Mars exploration rovers at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) February 10, 2003 in Pasadena, California. The identical robotic explorers, Spirit and Opportunity, will trek up to 109 yards each Martian day, far more than the much smaller Mars Pathfinder was able to do in 1997. The rovers will search for evidence of liquid water in two separate areas of the red planet. The rovers stand about five feet tall and weigh in around 400 pounds. The first rover has a launch opportunity May 30, 2003 and the second June 25, 2003.
This 3-D image released by NASA January 23,, 2004 combines computer-generated models of the Mars Exploration Rover Spirit and its lander with real surface data from the rover's panoramic camera. NASA made progress in fixing its malfunctioning Mars rover Spirit by finding a work-around for a balky memory card. "We made good progress overnight. The rover has been upgraded from critical to serious." said Peter Theisinger, rover project manager, at an afternoon press briefing 24 January at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). Theisinger said that ground controllers have established an ability to communicate with and control the vehicle reliably. Scientists said they managed to reset Spirit's computer and put the rover into what's called "cripple" mode to bypass software problems. Still, the problems may prevent the rover from taking another drive on Mars for as long as three weeks.
In this handout image provided by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)/JPL, NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit took and returned this image on January 28, 2004, the first picture from Spirit since problems with communications began a week earlier. The image from the rover's front hazard identification camera shows the robotic arm extended to the rock called Adirondack. As it had been instructed a week earlier, the Moessbauer spectrometer, an instrument for identifying the minerals in rocks and soils, is still placed against the rock. Engineers are working to restore Spirit to working order so that the rover can resume the scientific exploration of its landing area.
This handout photo obtained on September 10, 2025, from NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS shows an image taken by NASA's Perseverance rover that shows "leopard spots" on a reddish rock nicknamed "Cheyava Falls" in Mars' Jerezo Crater in July 2024 on Mars. Colorful, speckled rocks found on the surface of Mars have offered among the most encouraging evidence yet of ancient life on our neighboring planet, scientists at NASA announced on September 10, 2025. The Perseverance Mars rover collected the "Sapphire Canyon" rock samples in July 2024 from the bed of what's considered an ancient lake, and its poppyseed and leopard-esque spots pointed to potential chemical reactions that piqued the interest of researchers.